Why are ocean freight rates so high in 2021? What can you do to make your business survive?
Shipping rates are a major factor in trade costs. The new hike in ocean freight rates creates an additional challenge to the world economy as it tries to recover from the worst global crises since the Great Depression (1929-1939).
Container rates impact global trade because all manufactured goods are shipped in containers.
Ocean freight costs have gone crazy. A case in point is the 1,300-foot giant container ship that got stuck in the Suez Canal on March 23, 2021, disrupting global trade to the tune of billions of dollars every day until it was refloated on March 29.
However, even before the blockade issues on the Suez Canal (the shortest route from Europe to Asia), ocean freight rates have already increased for goods out of China. Let me show why ocean freight ratings soar so high in 2021.
1.How Much Have Sea Freight Rates Increased?
Ocean freight rates to the US and Europe from China have increased more than 100%. Freight rates to the American West Coast and the UK have increased by over 200% over the first quarter of 2021.
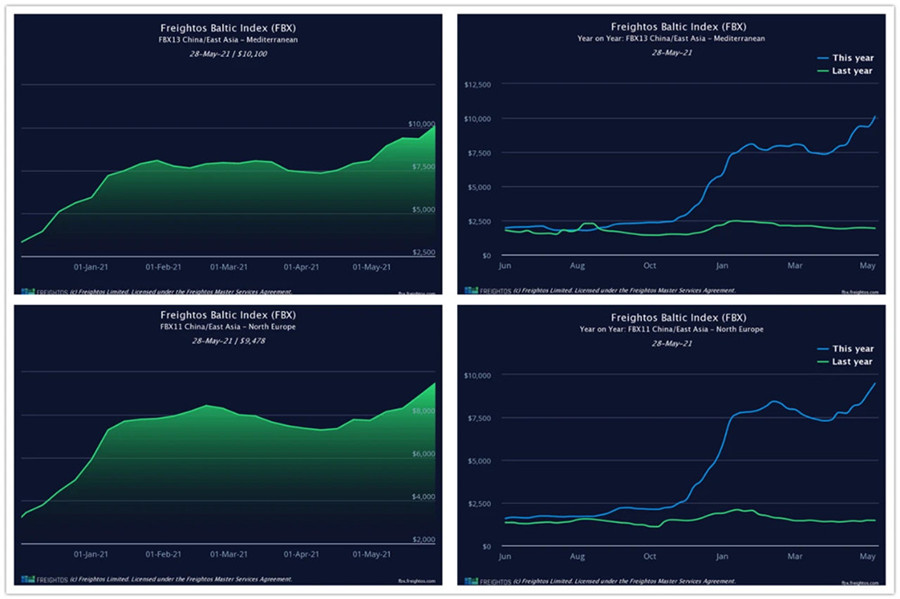
The Freightos Baltic Index pegs the rate of a 40-foot container high cube container from China to the US that cost about $4,000 four months ago has increased to $10,000. This is four times higher than it was in 2020. This is assuming that you can find a container and able to book space on a vessel.
Close to 60% of goods are shipped in containers and this extraordinary surge in container prices has impacted online retailers who are importing high-demand goods from China.
While the hike in ocean freight rates affects all businesses that ship goods, the eCommerce industry, and Western consumers may be most affected because most eCommerce sellers in the US and Europe import their goods from China.
Recently, the Asian to European Ocean Shipping Container Freight Index reached a new record, the index freight rate for the first time above $10,000, the actual freight rate has reached the ceiling of $15,000.
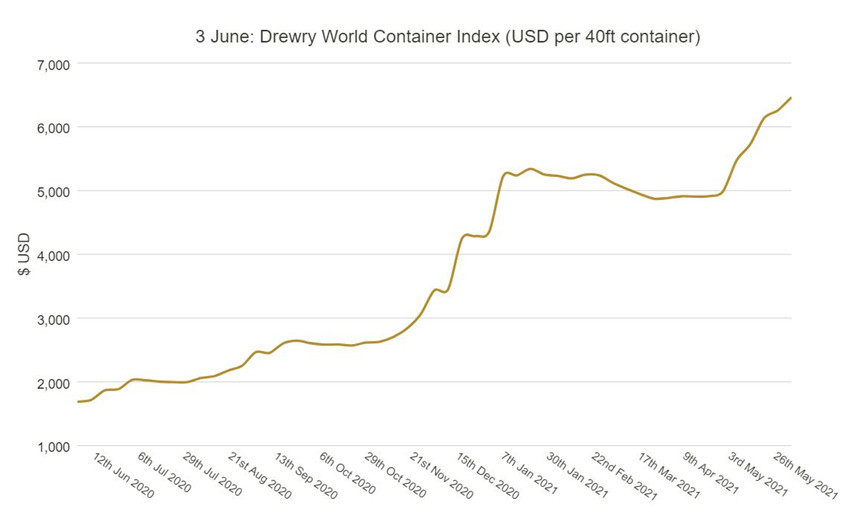
In the last week of May, Drury’s World Container Index (WCI) showed the cost of shipping a 40-foot container from Shanghai China to Rotterdam Holland rose 3.1% to $10,174, up from last week and up 485% from a year ago.
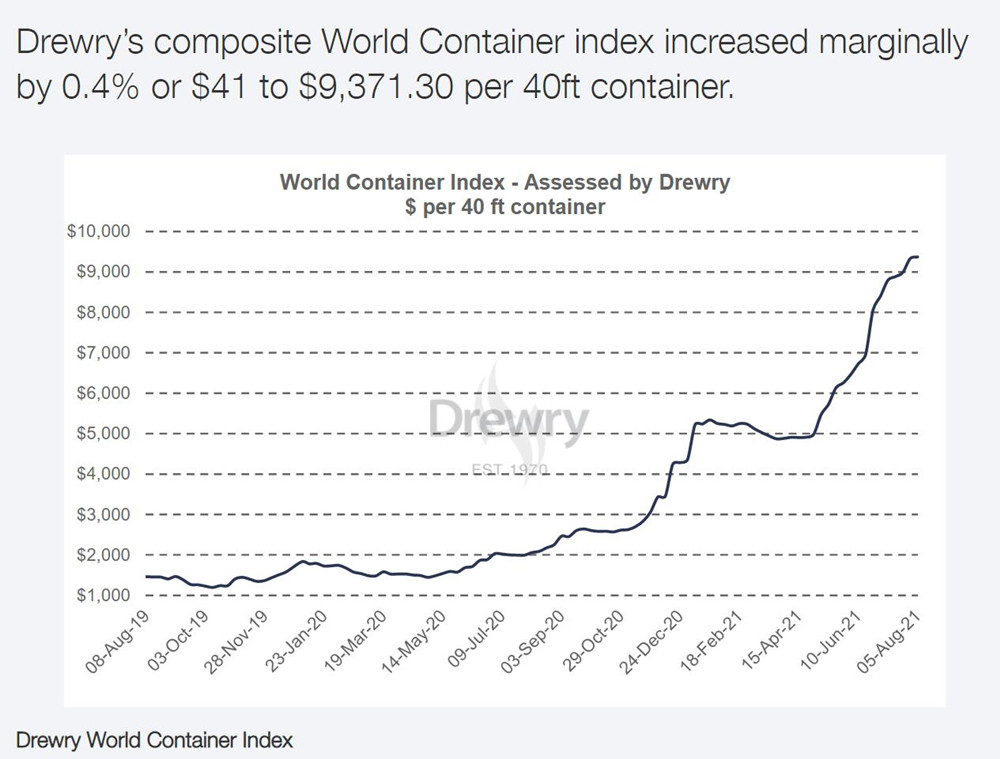
Update on 10th August,2021
Meanwhile, according to the Baltic (FBX) Freight Index, sea freight rates in Asia-northern Europe rose 9.1% to $9,871 per 40HQ container, while ocean freight in Asia-Mediterranean rose 6.1% to $10,214 per 40 feet.
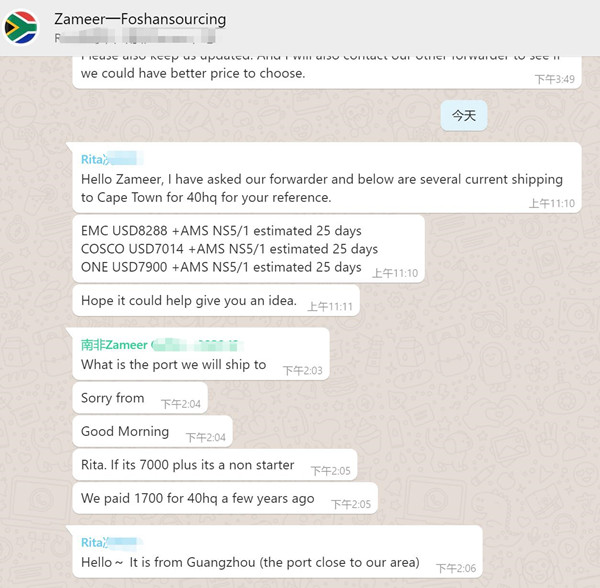
Taking one of our case as example,we exported to South Africa in 2019 with USD1700 per 40HQ container.However,now it is around USD8000 each container.
The reality, of course, is that many customers are paying much more than that, with shipping companies increasingly charging extra fees such as guaranteed shipping space, which can easily reach $1,000 per case.Which means if you need to pay the guaranteed charge when booking the container.If you don’t load the container once getting the shipping order confirmation,the shipping company will not return back the guaranteed money.
2.Why are Sea Freight Rates so High in 2021?
The pandemic started off the surge in sea freight cost but there are other factors that contributed to the current high cost. It is important to note but these factors became apparent as an effect of the pandemic.
2.1 Fewer sailings
The Covid-19 pandemic shook global trade. The problem started in January 2020 when China locked down several parts of the country to restrain the spread of the virus infection. Factories in China that supply goods to businesses around the world stopped their operations. As a result, the volume of shipping fell.
Covid-19 spread across the world. Economies in almost all countries went to a halt or slowed down. Consumers were not buying, thus, there was a drop in the demand for many products and commodities. These left many sea carriers with empty spaces.
With less demand for container space, ocean liners had to cut down on their sailings. It was the most logical thing to do because they would be losing more money if they allowed their half-empty vessels to sail.
In the 4th quarter of 2021 and the 1st quarter of 2021, countries began re-opening their economies. Factories in China started to continue their operations. Consumers started to get back to shopping. With the increase in international trade volumes came greater demand for container spaces in vessels and, therefore, an increase in sea freight rates.
Although the demand for container spaces continued to rise, ocean liners continued to do “black sailings.” Blank sailing is a term used to refer to no sailing or canceled sailing. Ocean lines create blank sailing by canceling previously scheduled sailings. Blank sailing is done to reduce the capacity and increase ocean freight rates.
Ocean liners informed shippers they either canceled sailings or their vessels would skip certain ports of call.
In April 2020, The Journal of Commerce said THE Alliance of Hapag-Lloyd, Ocean Network Express, Yang Ming, and the 2M Alliance (Maersk Lines and the Mediterranean Shipping Co said 75 sailings will be canceled until September. This was to match capacity with weak projected container volumes.
By June 2020, the Sea-Intelligence Maritime Consulting said there were 126 void sailings between Asia and North America through August because of the impact of the pandemic on container volumes. There were also 94 blanked sailings on the Asia-Europe routes.
This shows that ocean carriers are still not confident that the demand for container spaces will remain strong. They have started to restore some capacity but still not enough to meet the demand causing a rise in ocean freight rates. The hardest hit is Asia to the US route but ocean freight rates have also increases in Europe to US routes.
Blank sailing brings a lot of uncertainty. Your container for shipment may have to wait longer than usual to get a vessel space. It may also be that your container already has a booked space but the ocean liner may at the last minute cancel the sailing.
2.2 Container shortage
Shippers have to wait for weeks for empty containers to be available and are paying premium rates to get hold of them. Many shippers scampering for empty containers have caused shipping costs to soar. The shortage of empty containers is not only driving up shipping cost but also delaying the shipment of goods from China.
Chinese factories are once again in full operations producing products for the world. Demand for outbound capacity from China and Far East ports is almost at its peak. Ocean carriers, however, are still canceling sailings increasing freight rates for insufficient space on the Far East to US route.

An ocean carrier can charge, for instance, more to ship a loaded container from Guangzhou to Los Angeles than from Los Angeles to Guangzhou. This is so because shipping containers from China to the US or Europe has a high demand prompting ocean liners to want to immediately ship empty containers back to Asia.
Ocean liners do not want to waste so much time getting the containers filled in the US. As soon as the US consignees unload and return the containers, many of them are shipped empty to the Far East. The same thing happens in trade between Europe and China.
There is an intense shortage of empty containers in the US that in the last quarter of 2020, the Federal Maritime Commission (FMC) was prompted to look into the possible violation of the Shipping Act of 1984 by the ocean liners.
2.3 Lines add surcharges to ocean freight rates
This 2021, Asian ports are seeing a high demand for vessel space and equipment so much so that importers are paying as much as 50% more than the already higher rates just to get their shipments to the US.
The rampant shortage of empty containers, speeding the return of empty containers to the Far East, and cutting sailings are some of the scenarios shippers have to contend with right now. Additionally, some ocean liners have also enforced new surcharges.
- Container Retention Surcharge was imposed on December 2020 by the Orient Overseas Container Line (OOCL), a Hong Kong-based container shipping and logistics service company. The company added a $300 charge for every 20ft container and $500 for each 40ft or 45ft container. This is applied to dry containers (only for dry goods / without temperature controls).
- Equipment Imbalance Surcharge was imposed on January 2021 by Hapag-Lloyd. This is an additional surcharge of $200 for each 40ft container on exports from North Europe to the UDS.
The ocean carriers say these additional surcharges were due to container shortage. Unfortunately, they were the ones who help create the shortage that resulted in these new charges. Regardless of the cause, shippers still need to pay more to ship their cargoes.
2.4 How COVID-19 has changed consumer behavior
Due to the COVID-19 pandemic, people are living, buying, and thinking differently. The pandemic has driven consumers to change their routines, as well as to adapt to new habits and behaviors. Many say these new behaviors will continue post-pandemic.
Buying online has been the norm because of health concerns and lockdown restrictions that have forced people to stay in their homes. Home offices and home gyms have become common. All these have been set up by ordering stuff online. Even buying essential goods and ordering food are strictly done online.
While most consumers have been shopping online, many of them have become more judicious on their purchases.
With the vaccine rollout now in place and lockdown restrictions have been eased up, many consumers are dying to go shopping again. Consumers are now spending on things they forewent during the lockdown period including apparel, beauty products, and electronics. These goods are now the most in-demand for consumers’ discretionary spending, post-pandemic.
The increase in online retail came with an increase in ocean freight rates. The increased demand for some goods meant retailers have to deal with increasing ocean freight costs.
2.5 China’s trade surplus
China produces a lot of consumer goods at costs lower than other countries. The United States is one of China’s top importers. On the other hand, the US exports to China soybeans, industrial machines, crude oil, semiconductors, and passenger cars.
Currently, the demand for China-made products has reached record high. The increase in eCommerce sales and lockdown restrictions has forced many ships and empty containers to remain idle in ports. Since China is one of the first economies to recover from the pandemic, it is exporting more goods to the Western market than importing goods from them.
The increased demand for China exports has made it more profitable for ocean liners to simply send empty containers back to China than fill them up with China imports. Add to the fact that China exports are often high-value goods while US exports are just low-value agricultural products such as soybeans. When Western economies bounce back, competition over empty containers increased ocean freight rates.
As an example: China exports two containers to the US filled with iPhones. Those containers are supposed to be filled with soybeans and shipped back to China. A trade deficit happens China does not two containers full of soybeans.
From the point of view of China, there is a Trade Surplus because its export outweighs its import. From the point of view of the US, there is a Trade Deficit because its import exceeds its exports. The port of LA, as of today, receives 3 ½ containers from China for every container it ships back to China.
A trade imbalance is common between China and the US and other countries. In the first quarter of 2021, when most Western economies are just starting to recover from the pandemic, China’s exports rose 60.6% because of the high demand for Chinese goods.
In the first quarter of 2021, China had a global trade surplus of USD 103.25 billion as compared to its trade deficit of USD 7.21 billion in 2020.
2.6 US-China’s trade war
The US-China Trade War started in 2018 when the US imposed a 25% tariff on China imports worth USD 34 billion.
The US and China imposed additional tariffs on goods imported from the other country (China to the US and the US to China). This means the US buyers need to pay higher import taxes for goods from China and vice-versa.
In 2019, the US imposed tariffs on over USD 360 billion worth of Chinese goods. China, on the other hand, also imposed import duties worth about USD 10 billion on US goods.
With the change in administration in the US, there is today an uncertainty regarding tariffs the US will impose on Chinese goods. As a result, Chinese exporters are rushing to ship their goods to the US before new tariff schedules will be imposed. This is another reason for the sudden increase in ocean freight rates last year.
2.7 Global Cargo Traffic Jam
- Since the Covid-19 pandemic, people can’t always go out to movies, concerts, restaurants as usual. They are turning to online shopping, which has led to more goods being imported from China than before, and a shortage of containers.
- In some of the more affected countries, their semi-closed ports have left many ships unable to unload in time after landing.
In some countries with benefits, supply chain bottlenecks have been caused by increased unemployment benefits and shortages of trucks and drivers.
3.What You Can Do to Protect Your Business?
Mostly, eCommerce retailers are the most affected by the increased ocean freight rates. Sadly, this added cost could be or could not be passed on to consumers. Whether eCommerce retailers will pass the added cost to the consumers or not, it is bad for business.
Here are some things that can help protect your business from the impact of higher ocean freight rates:
- Plan Your Shipments Early
Now, more than ever is the best time to plan your buying schedule and book your cargo early. Make a feasible buying and shipping plan ensuring you do not run out of stock. This means you should always be on top of your inventory.
You should book your cargo early, weeks or even months ahead. Avoid booking your cargo during the holidays and peak seasons.
- Work With a Reliable Freight Forwarder
It always pays to work with a reliable freight forwarder. Your freight forwarder can do so much to protect your business. It is best to work with an established and large freight forwarding company because they have more resources and can more effectively deal on your behalf.
Make sure your freight forward is transparent and communicates with you all matters concerning your shipment.
Regulators of the US shipping industry have started to look into detrimental shipping practices to reduce factors that are responsible for the recent rise in ocean freight rates.
- Consider Your Alternatives
So far, there is only a small price difference in ocean freight rates between 20ft and 40ft containers. Increasing your order and ship a 40ft container will lower the price per unit of your products. If your shipment is less than 25 cubic meters (CBM), Less a Container Load (LCL) is becoming a more feasible option.
Despite the current high cost of ocean freight rates, air freight is still much more expensive. The difference in cost is, however, has slightly narrowed and there may be instances when air freight is more viable especially when you need to reduce stock outrages and optimize your cash flow.
4.When Will Sea Freight Rates Go Back to Normal?
Asia to the US ocean freight rates are almost or at all-time highs. While different freight indices have different numbers, there is a similar trend – they are either up or steady on top.
Nobody knows when ocean sea freight rates will get back to normal. There are some reports that say ocean freight rates will remain high until Q4 of 2022. If you are an eCommerce retailer and are shipping high demands and fast-moving goods because of the pandemic, this may sound like a very long wait.
Others say that because of the continued shortage of empty containers despite most ocean carriers ordering new containers, container shortages will continue throughout 2021.
5.Conclusion
There seems to be no light at the end of the tunnel as of the moment as far as the increased ocean freight rates are concerned.
Knowing the reasons for such an and why ocean freight is more complex right now can help you more effectively plan and prepare your buying program.
Contact us if you would like to know the latest ocean freights shipping from China to your countries.
CONTACT US
Tell us Your Project Details and Get a Quick Quote Right Now , Please Feel Free to WhatsApp: +86-13790051345










Leave A Comment